With the continuous expansion of the installed capacity of photovoltaic power plants throughout the country, and advantageous resources being seized by various companies in the industry, the development of photovoltaic power plants will be increasingly difficult, and production and maintenance management at the end of the industrial chain will gradually show its importance. The level of production operation and maintenance management will directly affect the overall economic efficiency and profitability of photovoltaic companies, and it will surely become a key factor supporting the safety, economy, and long-term development of the photovoltaic industry.
Photovoltaic power generation production management mainly includes: production operation and maintenance management (integrated operation and maintenance management), safety and quality management, power generation planning and power marketing management, overhaul and rapid response management, material storage management, production training and authorization management and documentation. Information management. Production operation and maintenance management are the core of the production field. Other management means assist in production operation and maintenance management. Each section is complementary to each other. Figure 1:
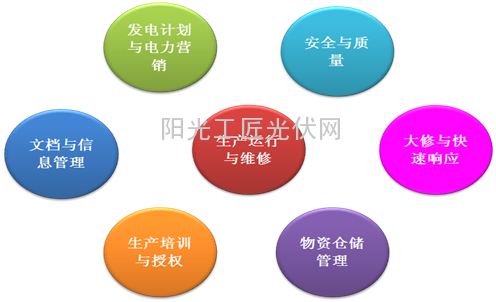
Figure 1 Production Operation and Maintenance System Architecture
First, production operation and maintenance management
Operation management
(1) Work ticket management
Work tickets play an important role in the safety risk control and maintenance quality control in the process of equipment deficiencies. The preparation of work tickets requires detailed steps to eliminate the equipment defect, identify the safety risks (personnel safety and equipment safety) of the entire process of elimination work, and do a good job in risk pre-judgment work, which mainly includes: work location (function location and work location of equipment) ), Prerequisites for start of work, work steps, QC control points, schedules, person in charge of work, members of working groups, work risks and countermeasures, spare parts (must change parts and exchangeable parts), tools (common tools and instrumentation), etc.; The work ticket controls the key points in the work process, and combines the functions of the QC inspector in quality management to set the W point (witness point) and H point (stop work check point) to ensure the work quality; the work ticket needs to be strictly executed during execution The requirements for safety and quality are strictly controlled; work records and completion reports must be kept after the work ticket has been executed.
(2) Operation ticket management
The ticket is used at any point in the operation of the plant equipment. Operation instructions should be made clear. The switching operation is generally performed by two people. The operator and the guardian share the responsibility for the operation. After verification of the functional location, isolation of the boundary, operation instructions, and risk points, the operation is performed one by one according to the operation ticket. All operating specifications should comply with the "National Grid Switching Operation Requirements."
(3) Operation Record Management
The operation records are divided into two parts: paper records and electronic records. The paper records are mainly operation logs. The operation logs record the main work contents of the power station on duty, power plant output, accumulated power, fault losses, power loss, inspection, defects and abnormal conditions. , the use of important spare parts, etc.; after the completion of the daily work should be recorded in the power plant management system on the day the overall situation of the operation of the power station, the paper log should be properly preserved. The records of monitoring of the power plant monitoring and automatic control devices shall be checked daily for the integrity of the records and properly stored in the back office server (information storage device or enterprise private cloud).
(4) Handover Management
The power station shift team shall comprehensively transfer information such as power plant information, dispatch plans, spare parts usage, tool borrowing, key usage, and abnormal conditions, to ensure that the succession team obtains comprehensive information of the power station; the succession team shall check all power station information with the shift team. True and Accuracy. After the confirmation of the succession of the succession team is complete and error-free, they are signed and confirmed on the shift schedule together with the length of the shift shift team to complete the shift shift.
(5) Inspection Management
Inspection is divided into daily inspections, regular inspections, and spot inspections. The daily inspections are routine work of station attendants. Inspections, inspections, meter readings, etc. are performed on the power station equipment according to the inspection route. The attendants should have The ability to determine the type, level, and severity of the fault, and to find out the anomalies are reported and disposed of in accordance with the relevant procedures stipulated in the inspection management. At the same time, the anomalies should be recorded in the operation log. Regular inspections are aimed at the targeted inspection of the climate and special weather conditions of the site where the photovoltaic power station is constructed. Spot inspections are means for strengthening inspection and inspection of important sensitive equipment to ensure the reliable operation of important equipment.
(6) Power Station Key Management
The safety status of the power plant equipment key plays a crucial role in the operation safety of the power plant. The keys of the power plant key and the key of the plant key, and the key of the power plant are divided into two sets of management, namely, the keys for normal borrowing and the emergency key. The emergency key is saved by the on-duty station owner. Normally borrowed keys are borrowed and returned in response to real name registration. All users should use the key in accordance with the regulations. The key to the equipment should be equipped with a master key. The master key can be used only when approved by the headmaster in case of an emergency. In other cases, the master key must not be used.
(7) Electricity report management
The value of the power station should be reported to the headquarters at the end of each month. Monthly cumulative power information should be kept consistent with the operation log. The cumulative monthly loss power information should be consistent with the equipment power loss information. After the power information table is completed, the power station owner should review the power information and submit it to the headquarters for submission. The format should meet the management requirements of the headquarters, and the information reported should be true and accurate.
Maintenance management
(1) Work Process Management
Work process management is to standardize the work behavior guidelines for power station employees. Any personnel at the power station performing on-site work should follow the power station work process management to ensure the work order of the power station. The work process management includes: the normal work flow of the power station, emergency work flow, work behavior specification, pre-construction work, work application, work document preparation, work permit processing flow, execution and re-appraisal of work, completion report preparation, and so on.
(2) Preventive maintenance management
Preventive maintenance means that the power plant has planned maintenance and repair activities. Preventive maintenance management includes: confirmation of preventive maintenance items and maintenance intervals, preparation of preventive maintenance outlines, preparation of preventive maintenance plans, preventive maintenance preparations, power outage plans, power outage application processes, daily preventive maintenance, overhaul preventive maintenance, Preventive maintenance equivalence, component cleaning planning, preventive maintenance implementation, and preventive maintenance data management.
(3) Corrective Maintenance Management
Corrective maintenance refers to maintenance activities that occur when an unexpected failure occurs. The main categories of corrective maintenance are on-line maintenance and off-line maintenance. According to the response time, there are: temporary maintenance, repair, and repair. According to the maintenance level, there are: partial maintenance, overall maintenance, replacement of parts, and replacement of equipment. The main considerations for corrective maintenance are: the impact of the failure of the equipment on its system, the impact of the system on the unit and the plant, the short-term and long-term effects of the presence of the defect on the equipment, and the potential of the equipment after the failure Consequences; Impact of faulty or defective equipment on industrial safety and external grids. The object of corrective maintenance is generally an emergency that must be dealt with urgently. There are fewer isolation boundaries and high maintenance requirements. Corrective maintenance needs to quickly determine the cause of failure, accurately find the point of failure, do a good job of safety protection measures, and eliminate the failure protection in time. The system and power station are operating normally.
(4) Technical Supervision Test Management
The purpose of the technical supervision test is to use advanced test management methods to monitor and control the health and safety, quality, and economic performance of important parameters related to the operation of the power plant in accordance with national and industry-related standards and procedures. In a safe, high-quality, economical working environment. The power station needs to formulate a technical supervision plan, determine the test items, cycle, test standards, test equipment, personnel qualifications and risk points, strictly implement the test standards in the implementation process, report on the truthful technical supervision test, the power station should save the technical supervision test report, technical supervision test The data should be compared with the design parameters and evaluate the safety and reliability of the plant equipment and systems.
3. Production preparation management
Preparation for production is all preparation work during the operation period of the power station during construction, mainly during commissioning of the power station. Operators of power station operation and maintenance personnel can get involved in the commissioning phase of the project in advance to become more familiar with the performance of the power plant equipment, fault history, and supervise the construction quality. The construction problems during the power station project are proposed and eliminated in time before the grid connection. The preparations for production mainly include: production preparation plan preparation, preparation of production preparation outlines, preparation of power plant operation regulations, preparation of power station maintenance regulations, installation and participation, commissioning and participation, personnel training and authorized posts, establishment of wall systems, establishment of equipment accounts, and equipment placards. Production and production of material preparations (eg legal procedures procurement, record book, safety production identification, tools, spare parts, consumables, labor insurance supplies, etc.), technical data collection and arrangement, equipment handover preparation, commissioning work, communication network and telephone construction , living area material preparation and so on.
4. Transfer of production management
Transfer of power plants to power plants includes pre-transmission preparation of power plants, mandatory investigation, equipment handover, plant handover, operation transfer management, legacy item management, transfer site safety management, key transfer management, file transfer management, spare parts and tools (common tools, special Tools, metering instruments, etc. are handed over to management; among them, management of legacy items is a difficult task for the entire transfer. Manufacturers and constructors need to specify who is responsible for the disposal of the remaining items and the completion time. For those engineering units that cannot complete the vacancy on time, The construction fee is used as a deficiencies, and the vacancy is completed by the manufacturer. Prior to the transfer, the power station must check necessary items. Only after all necessary items are qualified can the transfer activities be started. Acceptance of qualified items is taken over by the manufacturer to the production and operation stage.
5. Production Insurance and Claims Management
In order to ensure the normal operation of the power station and reduce the power loss or business interruption caused by various factors, it is recommended that the power station purchase production-related insurance. The main purchase insurance is business interruption insurance, disaster insurance, equipment quality insurance, etc., which are selected through risk and economic analysis. The amount and type of purchase; insurance needs to be purchased in full year by year to reduce the risk of claims in case of accidents. The power station needs to formulate a corresponding system according to the type of insurance purchased to guarantee the collection of evidence for claims under unexpected circumstances.
MIDI CALICUM PHOSPHATE (Feed Grade) is derived from phosphate rock, in a carefully controlled the chemical process which enhances biological availability, drives off fluorine and physically conditions the product for feed mixing. It is a source of highly available Phosphorus (P) and Calcium (Ca) that will help meet animal and poultry requirements for these essential nutrients. Calcium Phosphate, chemical structure This product is a mixture of different forms of calcium phosphate. Insoluble in ethanol and acetone, slightly soluble in water, soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid and nitric acid. Can be used as an anti-caking agent, acidity regulator, nutritional supplement, flavoring agent, stabilizer, moisture retention agent.
Calcium Phosphate Granular With OEM Formula
Calcium Phosphate Fertilizer,Dcp Granular,Calcium Phosphate Granular,Dicalcium Phosphate With Bentonite
MIDI FEED BIOTECH LIMITED , https://www.midifeed.com