Abstract: Optimizing the selection of tools according to the workpiece, including tool material, tool geometry, tool structure, cutting parameters and machine cutting data, will be related to production efficiency, production cost and processing quality. Establishing a cutting database and providing reasonable or optimized cutting quantities to the machinery manufacturing industry is one of the most effective measures to enhance the competitiveness of enterprises. This paper combines the research and development status of cutting database at home and abroad, discusses the core technology of cutting database, analyzes the problems in the research and application of cutting database, and focuses on the development trend of cutting database. It points out that the future research direction of cutting database will be integration, Intelligent, practical, networked and standardized.
1 Proposal of cutting database
Cutting data is a basic measure of the level of cutting technology. With reasonable cutting data, the functions of cutting machine and cutting tool can be fully utilized. Especially for various automatic machining machines, CNC machine tools and machining centers, the auxiliary machining time of automatic machining has been greatly shortened, so that in the effective processing time Making full use of reasonable or optimized cutting data is even more important to improve the economics of the entire processing system. Cutting data has traditionally been determined based on cutting manuals, production practice data, or cutting tests. The data source in the cutting manual is the most extensive, and the rationality is generally strong, but the pertinence and accuracy are poor. The data obtained by consulting the cutting manual is very insufficient in the advancement of the amount of information and methods; the production practice data is specific. For the application enterprise, the pertinence is strong, but the data is too scattered and lacks regularity; the data obtained through the cutting test is the most targeted, but subject to various limitations of the test conditions, the amount of data is extremely limited, and the test conditions are Production site conditions often vary widely.With the development of science and technology, the application of computers in cutting processing is increasing. Domestic and foreign computers have used computers to build cutting databases. The data and information needed for cutting processing are stored in the computer according to certain rules. , print, you can also modify, add and delete at any time. The contents of the cutting database shall include the recommended values ​​for the cutting amount. According to the processing conditions, the cutting speed under different life tools is recommended under different cutting depth-feed ratio combinations, and the power consumption is calculated. In addition, the grades, composition, properties of the workpiece and tool materials, and the model and performance parameters of the machine tool should be included. Because the computer stored data is highly dense, occupying a small space, easy to modify, add and delete, so the data required for cutting, even the curve and regression formula of the cutting experiment (such as Taylor formula, cutting force empirical formula, etc.), mathematical model, etc. Can be stored in the database.
| country | Name database | Database use | Cutting data source | Type of data |
| Belgium | CRIF | &mibrot; | car | |
| France | CETIM | o | Car drilling and milling | |
| Germany | INFOS | o | SPL | Car drilling and milling |
| Japan | TRI | &mibrot; | SPL | Car drilling and milling |
| Norway | SINTEF | &mibrot; | ||
| Sweden | &mibrot; | |||
| United Kingdom | PERAM ACBANK | o | Car drilling and milling | |
| United States | CUTDATA | o | PL | Car drilling and milling |
| Germany | SWS | o | SPL | Car drilling and milling |
| Israel | TECHNION | o | PL | Car drilling and milling |
| India | DATA MDC | o | SPL | Car drilling and milling |
| Sweden | CRVEFCOROCUT | &mibrot; | SP | Car drilling and milling |
| &mibrot; preparation for construction; o put into use; S-lab collection; P-production workshop collection; L-document data collection | ||||
2 Development status of cutting database at home and abroad
Since the birth of the first cutting database, most of the industrialized countries in the world have developed their own metal cutting databases. According to incomplete statistics, more than 30 metal cutting databases have been established in 12 countries including Germany, the United States, Sweden, the United Kingdom, Japan, Norway, Belgium and Hungary to provide various forms of information services. The survey of cutting databases in countries around the world (see Table 1) shows that the data in the current cutting database comes from laboratories, production workshops and literature, mainly used for turning, milling, drilling and grinding.Among the established cutting databases, CUTDATA and INFOS are the most famous. In 1964, the United States Metal Cutting Joint Research Corporation and the US Air Force Materials Laboratory jointly established the US Air Force Processability Data Center (AFMDC). The CUTDATA cutting database developed by the center is the world's first metal cutting database. The database contains a large number of cutting test data, and has been updated multiple times, more comprehensive and reliable, can be more than 3,750 kinds of workpiece materials, 22 kinds of processing The cutting parameters are available in 12 ways and 12 tool materials. Germany established the Cutting Data Information Center (INFOS) in 1971. The center stores more than 2 million pieces of single-data data processing information, making it one of the world's most cutting data databases with the most complete software information and the most complete data service capabilities.
The cutting database established in China began in the 1980s. At present, there are domestic research institutes such as Chengdu Tool Research Institute, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Shanghai University of Technology, Shandong University, Harbin University of Science and Technology, and Tianjin University.
Chengdu Tool Research Institute built the first experimental turning database TRN10 in China in 1987, and introduced the INFOS turning database software (called ATRN90 after domestic operation) from the then Federal Republic of Germany in 1988, and improved it. Introduced its revised version of the ATRN90E to the country. Subsequently, the development and introduction of the turning database software CTRN90V1.0 was continued. Compared with the original INFOS, CTRN90 improves and expands the system, enhances the function, adds Chinese data, and applies the concept of “processable material group – cutting material pair†to realize the Chineseization and Englishization of the software. It runs in the Chinese VAX/CVMS operating system environment, and the user interface is a human-machine dialogue mode, which uses a multi-layer menu driver. The software itself is about 8MB in size with 11 dedicated subroutine libraries. It uses domestic machine tools, tools and test data, as well as some foreign data. The CTRN90V2.0 was introduced in 1991 and the CTRN90V3.0 was introduced in 1992. Based on the above, in 1998, the database software running in the Windows environment was developed.
Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics is a relatively early university researching metal cutting database. As early as 1986, Professor Zhang Youwei of China Southern Airlines discussed some problems in establishing a metal cutting database. Xu Hongchang and others conducted further research on the metal cutting database. In recent years, the focus has been on the optimization of cutting data and the application of expert system technology in cutting databases. In 1988, a special cutting database software system NAIMDS was developed. In 1991, the KBMDBS cutting database system was further developed.
Beijing Institute of Technology has established a cutting database system for carbide tooling materials and coating tool manufacturers. According to the different sources and characteristics of the cutting data, they are divided into three categories: concentrated cutting data, discrete cutting data and data cutting data. Beijing Institute of Technology studied the storage and drawing of the cutting test curve in the cutting database, and on this basis, realized the storage and drawing of six test curves such as tool wear, tool life, chip breaking and cutting force, so that metal cutting The database is functionally capable of not only storing data, but also processing curves. This has positive implications for enriching the content of the cutting database, expanding the scope of the cutting database, and establishing the engineering database.
In addition to the establishment of their own cutting database in various countries, international academic institutions have also carried out research and development work on cutting databases, such as the International Production Engineering Society (CIRP) cutting processing model research group established in 1995, engaged in research on cutting processing prediction models. Providing cutting parameters for the machinery manufacturing industry, since 1998, invited world-renowned research institutions to join the research and establishment of its cutting database.
The economic benefits of the establishment of the cutting database are very substantial. In the early days of CUTDATA's database building, it saved $160 million for the industrial sector. INFOS can reduce the production time of a single piece by 10% and the production cost by 10%. SWS is used by more than 300 companies, saving an average of 15% to 40% of working hours per year. According to CIRP's survey of the economic benefits of cutting databases, cutting databases can reduce processing costs by more than 10%.
3 Establish the core technology of cutting database
The establishment of the cutting database includes structural design and application software design. The cutting database structure design includes the acquisition, processing and evaluation of cutting data, the establishment of cutting data, the optimization of cutting data, the output of cutting data and information services. Based on the characteristics of the post-evaluation cutting data, a discrete cutting database or a concentrated cutting database can be established.The data volume of the discrete cutting database is very large, involving many factors such as cutting method, workpiece material, tool material and its geometric parameters and structure, cutting parameters, cutting fluid and machine tool, and manages the data in the way of storage retrieval. In the conceptual structure design of the database, the (entity-relationship) model of the cutting data is first established, and then the logical structure design and the physical structure design are performed. The influencing factors related to the cutting data in the discrete cutting database are generally represented by codes, and the keywords in the cutting database are superimposed by the codes affecting the cutting data selection. Therefore, the keywords of various cutting methods are different, and their corresponding sub-libraries must be established separately. This is the sub-database technology for cutting databases. Each sub-library must consider that it can run under the master control program, and that it can run independently. It is built using a modular structure. Referential integrity should be established between the tables of the influencing factors in the database. The parent table and the child table have a constraint relationship. When the table is modified (insert, update or delete of the record), the computer automatically operates the corresponding table. Eliminate repetitive operations and errors that may result from it.
The Concentrated Cutting Database is used to store and manage the calculations of various cutting mathematical models, their coefficients and indices, and the machining conditions that produce these mathematical models.
The application management program for the cutting database should be able to meet the basic requirements of input, update, deletion, retrieval and output of cutting data. At present, the window menu display technology is often used, and the loop nesting is adopted in the programming, so that the system has considerable fault tolerance and error correction functions. In order to prevent the cutting database system from being easily retrieved and modified by other personnel to ensure the security of the database, the access can be controlled and the user can be authenticated. Only the correct user name and password can be used to have the right to use the database.
4 Problems and development direction of cutting database
The basic purpose of establishing a cutting database is to produce actual services, but the established cutting database and process database have not been put into practical use. The reasons for the analysis are various: 1 The enterprise pays insufficient attention to the cutting database; 2 Data The amount of information is not enough, and the problem of connection with CAPP, CAM and other systems has not been solved. 3 The key problem is that there are still some problems in the existing cutting database itself. First, the reliability of cutting data, due to the source of data, there are Data from the factory, laboratory data, and data from various manuals, which should undergo rigorous analysis, processing, and evaluation, otherwise, the application effect is inevitably poor. At the same time, there are problems with computer software. The strength of software functions is crucial to the role of data in the database. In order to further promote the application of cutting database, the cutting database is developing towards integration, intelligence, practicality and networking.- Integrated
- Intelligent
- Practical
- Networking
In order to conveniently and accurately query the manufacturing resources of the enterprise, the enterprise needs to establish a manufacturing resource database, which generally includes the basic definition and classification of the process, machine tools, tools, process equipment, blank types, material grades, material specifications, process rule libraries, and processes. Simple library, process parameter library (cutting parameters, equipment parameters, working time quota table) and typical process library. The cutting database is connected to CAPP, CAD/CAM and CIMS. As part of the manufacturing database, it provides reasonable cutting data for these automated manufacturing systems, from the cutting data center to the processing information center and even the production information center. Rules, rules, data and techniques are collected, evaluated, stored, processed and applied. Therefore, the cutting database is the basic data provider for NC machine tools, machining centers and CAD, CAM, CAPP, CIMS, etc., and is the basis for advanced technologies such as CAM, CAPP, and GT. Without the support of the database, there is no real computer integrated manufacturing system, so integration is an inevitable trend in the development of cutting databases.
The COATS system developed by the University of Pisa, Italy, for the selection of tools, is connected to the CAPP system, and its input data comes from other subsystems of CAPP. Some computer-aided design and manufacturing software developers have developed some cutting database modules. For example, UGCAM contains a powerful cutting database. Through database query, workpiece material, tool material, tool size parameters and cutting methods can be defined. The data of the spindle speed and the feed rate are obtained by the operation of the database. The UG CAM database consists of five sub-libraries: a workpiece material library, a tool material library, a tool size parameter library, a cutting method library, and a cutting speed library. The structure of the UGCAM database is shown in Figure 1. Tool materials are divided into five categories: high speed steel, uncoated solid carbide, uncoated indexable carbide, coated indexable carbide and coated high speed steel. There are four types of cutting methods: end milling, slotting, face milling and side milling. The tool types are: end mill, face milling cutter, T-shaped milling cutter, drum milling cutter, UG5 parameter milling cutter, UG7 parameter milling cutter and UG10 parameter milling cutter. The workpiece material types are: carbon steel, alloy steel, high speed steel, stainless steel, tool steel, aluminum alloy and copper alloy. Other CAD/CAM software, such as Pro/E, MasterCAM, Cimatron, etc., have also developed their own cutting database modules.
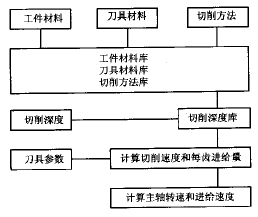 Figure 1 Structure of the UG CAM cutting database |
The data provided by the traditionally developed cutting database and tool management system are mostly “static†raw data, which are more specific and certain. Basically, they can only be counted as electronic manuals, and a wide variety of processing methods appear on the production site. Workpiece materials and tool materials with ever-changing performances are often difficult to solve with "static" databases. At present, the cutting database is developing in the direction of intelligence, using artificial intelligence to establish a cutting database to make it "dynamic". Since the database management system cannot perform logical reasoning or heuristic judgment from the stored data, the value of the stored data cannot be fully utilized, and the advantage of artificial intelligence can solve this problem. Combining artificial intelligence with a cutting database can solve some difficult problems in the cutting database. Intelligentization is the focus of cutting database research since the 1980s, and it is also the future development direction of cutting database.
Intelligentization is to store the experience of cutting experts, some general rules and special rules of cutting processing in the computer to achieve operation and decision-making. Many cutting techniques and their expert experience are difficult to express with rigorous mathematical models. Combining databases with artificial intelligence techniques is the best way to solve such problems.
The expert system consists of a knowledge base, an inference engine and a human-machine interface. The most critical part is the knowledge base and the inference engine. The knowledge representation of the COATS system uses production rules. In order to avoid the uncertainty that multiple rules are satisfied at the same time in the reasoning process, each rule is given a certain weight. The selection of tool parameters mainly depends on the rules and weights in the knowledge base, and is obtained through certain algorithm operations. The COATS system has approximately 300 rules written in the PROLOG language. The reasoning method of ESMDS, a cutting parameter selection expert system developed by Pennsylvania State University, is forward reasoning. The development language of the system is FORTRAN77. The University of Windsor Canada developed a machine tool and tool selection expert system based on part features. The system was developed with the expert system development tool EXSYS. The knowledge representation adopts production rules (122 in total) and the reasoning method is reverse reasoning. Yugoslavia developed an automatic tool selection expert system for generating rules and matrix method representation knowledge. The National “863†Program supports the cutting database and expert system (BYJC-CIMS-MDES) under the CIMS environment developed by Beijing Institute of Technology, integrating the cutting database and expert system services, and designing the knowledge base in the expert system. The combination of the database has achieved good results.
The expert system adopts rule matching reasoning, which is suitable for the field where causality is easy to find. Some phenomena in cutting processing are difficult to describe with regular knowledge and causality. Rule matching reasoning also needs to solve the problem of rule conflict. In addition, artificial neural networks, fuzzy algorithms, genetic genetic algorithms, etc. are used for computational reasoning of cutting data. In the UK, an intelligent grinding parameter selection system based on case-based reasoning is developed. Shandong University is developing tool materials based on case-based reasoning. High-speed cutting database for cutting parameter selection.
According to the theory of artificial intelligence, the higher the intelligence of intelligent systems, the greater the cost of system development. Therefore, the development and research of intelligent cutting databases should make full use of the existing scientific research results in the fields of intelligent technology and information science. The unique characteristics of the computer, thus developing a new intelligent cutting database to meet the requirements of enterprises for the rational use of cutting data.
The universal cutting database provides cutting process parameters for different machine tools, different cutting methods and different tool materials. It can provide a series of cutting parameters such as optimized tool angle, cutting speed, feed rate and cutting fluid according to different machining conditions. . However, the establishment of a universal cutting database is a huge project that requires a lot of manpower, material resources and capital. As a company, an industry, the tools and workpiece materials used are limited, and the basic cutting data can be obtained through data and tested. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a company's own database and it will not be too difficult.
Many tool manufacturers and research institutes have developed computer tool data management (TDM) systems, such as the TDMeasy software from Walter, Germany, to recommend the cutting parameters of the company's various tools for machining different workpiece materials. Walter's TDM tool management software has the ability to reduce planning time, minimize adjustment time and process interruption time, reduce tool types, facilitate tool standardization, reduce tool inventory, and control tool ordering. The AutoTAS tool management software developed by SandvikCoromant has 11 integrated modules. The software provides the company with CAD models (geometry, inspection, assembly) of more than 3,000 tools, automatically selecting the tool samples for use in the company's samples and electronic samples, providing inventory location, cost, supplier, and cutting for various tools. Performance, tool life and information on the workpiece to be machined. AutoTAS tool management software also provides tool inventory management, purchasing, statistical analysis, reporting, tool room planning and quality control.
Kennametal has also developed its own tool management software KATMS and ToolBoss. Datos Computer's tool supply software includes more than 30 tools and provides a wealth of information, and the calculated or acquired cutting data can be integrated into the software. Mapal's global tool management system can provide users with the right tool variety and quantity. It can establish a service department for users, and is responsible for the re-grinding, adjustment and distribution of tools, helping users to analyze and evaluate the machining process. Tool electronic samples from Gunther and Seco help users select and use cutting tools correctly. EMUGE FRANKEN's tool electronic samples can be used to calculate and analyze machining costs, as well as programming guides and G-code running procedures for multi-tools such as drill-and-thread tools.
CIM Germany has developed an electronic information system for metal cutting tools (on CDROM, commonly referred to as CIMSOURCE), which includes more than 115,000 tool data produced by 17 major tool companies worldwide. The CIMSOURCE system provides service to tool users, including standardizing graphics for tool users, optimizing tool management and optimizing the organization of large or batch tool supplies. The electronic catalog of the CIMSOURCE system helps users understand the wide range of products available in the world tool market and provides in-depth information for further preparation of specific processing processes. The tool supplier adopts the CIMSOURCE system to ensure that: 1 the tool is provided to the user accurately and on time; 2 because the supplied tool is in the form of electronic products, so the price is the best; 3 can expand the market and facilitate users to enter the world Trade network.
Many domestic research institutes and enterprises have researched and developed tool management systems, such as the national "863" program to fund CIMS-based computer-aided tool management system developed by Tsinghua University, and the computer tool management system developed by Jinan Qingqi Engine Factory for their own enterprises. . Northwestern Polytechnical University has also developed a database of 14 commonly used titanium alloy turning. Shanghai University of Technology has established a turning database for the oil industry. The Ministry of Aviation Industry has undertaken the preparation of aeronautical metal material cutting database. Harbin University of Science and Technology developed the PCBN tool cutting database. Shandong University is preparing to build a database of high-speed cutting database and ceramic tool cutting database and mold cutting processing. Tianjin University has cooperated with automobile manufacturers to establish a metal cutting database for automobile manufacturers. Shanghai Jiaotong University has established a rotary tool/cutting database.
The rapid development of Internet technology has brought new vitality to the field of cutting database applications. Networking emphasizes data exchange and resource sharing, which will be the main trend in the future development of cutting database technology.
At present, world-renowned tool manufacturing companies have opened their own websites. By visiting these websites, users can understand the company's profile, current production research, new product catalogs, features, quotations and publications, etc. Cutting parameters, some can download software, such as downloading standard tools and tool selection software for tool manufacturing, and tool CAD drawings. For example, Guhring offers free tool management software online. CIMSOURCE has also been integrated into the Internet and works in a conversational way to connect users around the world and keep getting information about cutting tools. CIMSOURCE can help solve the following tool manufacturing and use problems: cutting tool selection, cutting process, providing orders within the information network, tool graphic information, tool production and tool exit data.
While the cutting database is developing towards integration, intelligence, practicality and networking, on the one hand, it needs basic research on information model, data model, development design theory and model; on the other hand, cutting data should be carried out. The standardization work, the standardization of cutting data is the guarantee for the promotion and application of cutting database technology and stable development.
5 Conclusion
Combining the research and development status of cutting database at home and abroad, this paper analyzes the problems in the research and application of cutting database, focuses on the development trend of cutting database, and points out the future research direction of cutting database: cutting database should be integrated and intelligent , practical and network development; to carry out basic research on cutting database information model, data model, development design theory and model; at the same time, should also carry out standardization of cutting data, standardization of cutting data is cutting database technology Promote the application and the guarantee of stable development.
Due to the good thermal insulation performance, the application of Vacuum Glass For Buildings will achieve the dual effects of energy saving and environmental protection. ICESUN vacuum glass is energy saving vacuum glass. Ultra low energy consumption buildings such as passive rooms require good daylighting, thermal insulation performance of external windows at the same time. Different from traditional insulating glass by adding air layer or inert gas, the thermal insulation effect of the vacuum layer of vacuum glass(only 0.1 ~ 0.2mm thick between its two layers of glass) is twice that of triple insulating glass with low-e & argon and over ten times that of ordinary single pane glass. Tempered vacuum glass has the advantages of low U value of heat transfer coefficient, high visible light transmittance, adjustable total solar transmittance and light heat ratio, long service life, wide application area, good sound insulation and anti condensation performance.

Energy Saving Vacuum Glass,Energy Saving Low E Vacuum Glass,Power Saving Vacuum Glass,Energy Saving Vacuum Insulated Glass
ICESUN VACUUM GLASS LTD. , https://www.icesunvacuumglass.com