Foreword
This standard was drafted according to the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This standard is proposed and managed by the China Electricity Council.
This standard was drafted by: State Grid Corporation of China, China Electric Power Research Institute, State Grid Electric Power Research Institute, Fujian Electric Power Co., Ltd.
The main drafters of this standard: Qi Xu, Liu Chun, Zhao Haixiang, Qi Zheyi, Huang Zhen, Chen Mei, He Guoqing, Shi Wenhui, Zhu Lingzhi, Zhang Junjun, Chen Mozi, Chi Yongning, Feng Wei, Li Guanghui, Bao Wei, Zhao Weiran, Ju Rong Rong, Shi Tao, Wu Wenxuan.
1 Scope
This standard stipulates the general principles and technical requirements that photovoltaic power generation systems should follow in order to access the grid.
This standard applies to access to the grid through the 380 V voltage level, and through the 10 (6) kV voltage level access to the user side of the new construction, reconstruction and expansion of photovoltaic power generation system.
2 normative references
The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only dated versions apply to this document. For undated references, the latest version (including all amendments) applies to this document.
GB 2894 Safety Signs and Guidelines for Use Thereof
GB/T 12325 Power Quality Supply Voltage Deviation
GB/T 12326 power quality voltage fluctuations and flicker
GB/T 14549 Power Quality Public Power Harmonics
GB/T 15543 power quality three-phase voltage imbalance
GB/T 16895.32 Electrical installations of buildings - Part 7-712: Requirements for special installations or locations - Photovoltaic (PV) power supply systems
GB/T 17215.322 Particular requirements for alternating current measuring equipment Part 22: Static active energy meters ((0.2S class and 0.5S class)
General requirements for GB/T 19862 power quality monitoring equipment
GB/T 24337 Power Quality Harmonics Between Utility Grids
DL/T 448 electric energy metering device technical management regulations
DL/T 614 multi-function energy meter
DL/T 645 multi-function energy meter communication protocol
3 Terms and Definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this document.
3.1
Photovoltaic power generation system photovoltaic (PV) generation system
Utilizing the photovoltaic effect of photovoltaic cells, a solar power system that converts solar radiation directly into electrical energy.
3.2
Inverter
A device that converts DC power into AC power.
3.3
On-line point of the internet
For a photovoltaic power generation system with a booster station, it refers to a booster station high-voltage-side bus or node. For a photovoltaic power generation system without a booster station, it refers to the output aggregation point of the photovoltaic power generation system. The definition of the grid point can be found in Appendix A.
3.4
Islanding
Part of the power grid, which includes the load and power supply, continues to operate in isolation after being detached from the main network. Isolated islands can be divided into unplanned islands and planned islands.
Note: Unplanned islands are unplanned and uncontrolled islands. Planned islands refer to islands that are planned to take place according to pre-configured control strategies.
3.5
Anti-islanding
Prevent the occurrence of unplanned island phenomenon.
4 Reactive capacity and voltage regulation
4.1 Photovoltaic power system power factor should be continuously adjustable within a range of 0.95 to 0.95.
4.2 Within the range of reactive power output of the photovoltaic power generation system, it shall have the reactive power output adjusted according to the voltage level of the grid connection point and participate in the voltage adjustment of the power grid. The ability of the section, its adjustment method, and reference voltage and voltage adjustment rate can be set by the grid dispatching agency.
5 start
5. When the flying photovoltaic power generation system starts, the current grid frequency and voltage deviation status should be considered. When the grid frequency and voltage deviation exceed the normal operating range specified in this standard, the photovoltaic power generation system should not be started.
5.2 Photovoltaic power generation should not cause the power quality of the power grid to exceed the scope specified in this standard. At the same time, it should ensure that the rate of change of its output power does not exceed the maximum power change rate set by the power grid.
6 operational adaptability
6.1 Voltage Range
When the voltage of the PV power system grid point is between 90% and 110% of the nominal voltage, the PV power generation system should be able to operate normally.
6.2 Power Quality Range
When the photovoltaic power generation system connected to the grid voltage fluctuations and flicker values ​​to meet GB/T 12326, harmonic values ​​meet GB/T 14549, inter-harmonic values ​​meet GB/T 24337, three-phase voltage unbalance to meet GB/T 15543 When required, the PV system should be able to operate normally.
6.3 Frequency range
When the PV frequency of the PV system is within the range of 49.5Hz-50.2Hz, the PV system should be able to operate normally.
7 Power Quality
7.1 Basic requirements
7.1.1 The public connection points of the photovoltaic power generation system shall be installed with power quality online monitoring devices that meet the requirements of GB/T 19862.
7.1.2 The historical data of the power quality monitoring of the photovoltaic power generation system shall be kept for at least one year, and shall be invoked by the power supply network enterprise if necessary.
7.2 Voltage deviation
After the photovoltaic power generation system is connected, the voltage deviation of the public connection point of the connected person shall meet the requirements of GB/T 12325.
7.3 Voltage fluctuations and flicker
After the photovoltaic power generation system is connected, the voltage fluctuations and flicker values ​​of the public connection points of the connected people shall meet the requirements of GB/T 12326.
7.4 Harmonics
7.4.1 Harmonic injecting current of the public connection point of the photovoltaic power generation system shall meet the requirements of GB/T 14549. Including the permissible harmonic current of photovoltaic power generation system connected to the power system shall be installed according to the photovoltaic power generation system. The ratio of capacity to the total capacity of the sending/supplying equipment with harmonic sources at the common connection point is allocated.
7.4.2 After the photovoltaic power generation system is connected, the interharmonics of the connected public connection points shall meet the requirements of GB/T 24337.
7.5 Voltage Unbalance
After the photovoltaic power generation system is connected, the unbalanced voltage of the connected public connection points shall meet the requirements of GB/T 15543.
7.6 DC component
The direct current component of the photovoltaic power generation system injected into the public connection point should not exceed 0.5% of its AC rated value.
8 Security and Protection
8.1 Basic requirements
8.1.1 The protection of photovoltaic power generation system shall meet the requirements of reliability, selectivity, agility and quick motion, and comply with relevant standards and regulations.
8.1.2 Photovoltaic power generation system Switching devices that are easy to operate, lockable, and have a clear disconnection point should be installed at the output summary point of the inverter to ensure the personal safety of maintenance personnel of power facilities.
8.2 Low/High Voltage Protection
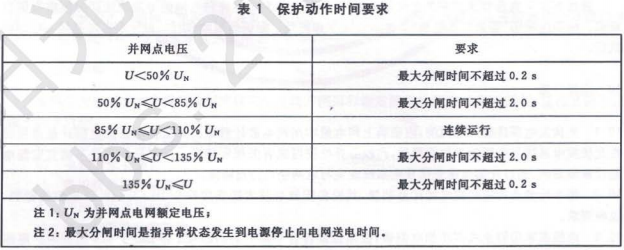
When the PV voltage of the photovoltaic power generation system exceeds the voltage range specified in Table 1, the transmission of power to the grid line shall be stopped within a corresponding period of time. This requirement applies to any phase in a multiphase system.
8.3 Frequency Protection
When the frequency of the grid-connected PV system exceeds 47.5 Hz to 50.2 Hz, power transmission to the grid line should be stopped within 0.2 s.
8.4 Anti-island protection
Photovoltaic systems should have the ability to rapidly monitor islands and immediately disconnect from the grid. Anti-island protection operation time is not more than 2s, and anti-island protection should also cooperate with grid-side line protection.
8.5 Reverse Power Protection
When the photovoltaic power generation system is designed to be irreversibly connected to the grid, reverse power protection equipment should be configured. When it is detected that the reverse current exceeds 5% of the rated output, the photovoltaic power generation system should automatically reduce the output or stop sending power to the grid line within 2 s.
8.6 Restore to the grid
After a disturbance occurs in the system, the PV system is not allowed to be connected to the grid before the grid voltage and frequency return to the normal range. After the system voltage frequency returns to normal, the PV system needs to go through an adjustable delay before it can be reconnected. The time can be set to 20s-5min, set by the local grid dispatching agency.
9 General technical requirements
9.1 Grounding
The grid-connected photovoltaic power generation system equipment should be grounded/connected to the protection line in accordance with the requirements of GB/T 16895.32.
9.2 Electromagnetic Compatibility
Photovoltaic power generation systems should have appropriate anti-electromagnetic interference capabilities, should ensure that signal transmission is not subject to electromagnetic interference, and the actuator does not malfunction. At the same time, the electromagnetic interference generated by the equipment itself should not exceed the relevant equipment standards.
9.3 pressure requirements
The equipment of the photovoltaic power generation system must meet the withstand voltage standard of electrical equipment of the corresponding voltage class.
9.4 Security Identification
With the photovoltaic power generation system connected to the grid with 380 V voltage level, the dedicated low-voltage switchgear connecting the photovoltaic power generation system and the power grid should have a prominent logo. The logo should indicate such warning words and symbols as "warning", "dual power". The shape, color, size and height of the logo comply with GB 2894.
10 energy metering
10.1 Before the photovoltaic power generation system is connected to the power grid, the on-grid power and net power metering points should be clearly defined. Photovoltaic power system power measurement points should be located at the property rights division of the photovoltaic power generation system and the power grid, and the division of property rights is determined according to the relevant regulations of the country. Where an electric energy metering device is not suitable for installation at the demarcation point of property, the metering point for the customs clearance shall be negotiated between the owner of the photovoltaic power generation system and the grid company.
10.2 Each metering point shall be equipped with an electric energy metering device. Its equipment configuration and technical requirements shall comply with DL/T 448, and relevant standards and regulations.
10.3 Watt-hour meter A static multi-function energy meter with technical performance in accordance with the requirements of GB/T 17215.322 and DL/T 614. The power meter should have at least bi-directional active power and four-quadrant reactive power metering functions and event recording functions. It is equipped with a standard communication interface and has the functions of local communication and remote communication through the power information collection terminal. The power meter communication protocol complies with DL/T 645.
10.4 The photovoltaic power generation system connected to the grid with a voltage rating of 10(6) kV shall be equipped with a set of primary and secondary watt-hour meters with the same type, same specification and accuracy as the same measurement point. The main and subsidiary tables should have clear signs.
10.5 The electric energy metering device shall be responsible for the ownership of the photovoltaic power generation system and be installed before the grid connection. The channels, protocols, and system commissioning shall be carried out in conjunction with the power information collection terminal and the master station system; the electric energy with corresponding qualifications shall be approved by both parties. The measurement and inspection institution completes relevant inspections on the electric energy metering device, issues a complete inspection report, applies seals, seals, or other sealing measures; before the electric energy metering device is put into operation, the grid company and the property right owner of the photovoltaic power generation system shall jointly complete the acceptance check.
11 Communication and Signals
11.1 Basic requirements
11.1.1 Photovoltaic power generation systems that pass 10(6) kV voltage level shall have the capability of data communication with the power dispatching agencies. The communication system of both sides of the grid should be based on the premise that the safe and economic operation of the grid must meet the requirements of the electric power communication business, and meet the requirements of electric power communication for relay protection, safety automatic devices, dispatch automation and dispatch telephones.
11.1.2 The communication method and information transmission between the photovoltaic power generation system and the power grid dispatching agency shall be stipulated by both parties after consultation, including the types of signals provided by each other, the method of providing signals, and the requirements for real-time performance.
11.2 Normal Operation Signal
In the case of a photovoltaic power generation system connected to the grid with a voltage rating of 10(6) kV, the signals provided by the photovoltaic power generation system to the grid dispatching organization shall include at least:
a) Grid-connected state of photovoltaic power generation system;
b) Photovoltaic power system active and reactive power output, power generation, power factor;
c) the voltage and frequency of the grid point and the current of the injection power system;
d) transformer tap position, main circuit breaker switching status, etc.
12 grid detection
12.1 Basic Requirements
12.1.1 The photovoltaic power generation system shall provide power grid companies with a test report on the operating characteristics of the photovoltaic power generation system within six months after the grid-connected operation.
12.1.2 Photovoltaic power generation system The detection point for access to the power grid is the photovoltaic power generation system connection point, which shall be carried out by a unit or department that has appropriate qualifications. The test plan shall be submitted to the power grid enterprise for record before the test.
12.2 Test Content
The inspection shall be conducted in accordance with the relevant standards or regulations formulated by the State or relevant industries for the grid-connected operation of the photovoltaic power generation system. It shall include but not be limited to the following:
a) Detection of reactive capacity and voltage regulation capability;
b) Power quality testing;
c) General technical condition detection;
d) Adaptability testing in grid operation;
e) Security and protection function detection.
Appendix A
(Informative Appendix)
Illustration of grid point legends
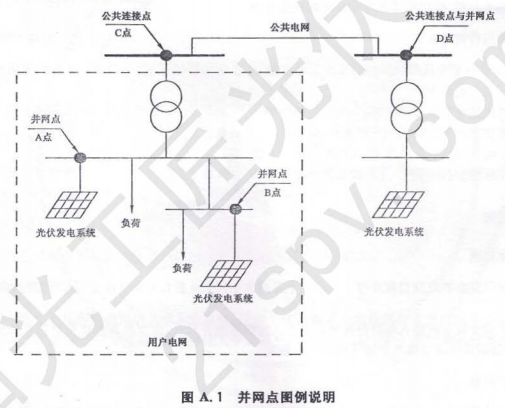
The grid connection point of photovoltaic power generation system refers to the connection point between the photovoltaic power generation system and the power grid. The power grid may be the public power grid or the user power grid.
The illustration of the grid point is illustrated in Figure A.1. The dashed box is the grid of the subscriber. The subscriber grid is connected to the public grid through the common connection point C. Within the user's power grid, there are two photovoltaic power generation systems, which are connected to the user's power grid through points A and B, respectively. Points A and B are point-of-grid connections, but they are not public connection points. At point D, there is a photovoltaic power generation system directly connected to the public power grid. Point D is the junction point and the public connection point.
Made of Die-cast aluminum housing and tempered glass, with isolated drivers, the outdoor landscaping lights are IP67 wateproof recessed underground.LED`s work well in rain, snow, and sleet. Suitable for both line voltage 110V 120V indoor and outdoor lighting.Applications include gardens, path, stadiums, passage,and other places. Lifespan of over 50,000 hours.100% environmentally-friendly. Low heat and input voltage. 100% safe for people. We provide 24 hour full time after-sale service on our rain waterproof exterior inground lights for outside house. Contact us with any questions. Jiangmen Synno Co., Ltd is a high and new-tech enterprise. Our company specialized in LED green light source. And we are engaged in medium and high-end LED decorative lighting with a whole set of design and manufacture of lamps and lanterns, development of control system and engineering supporting service. Our company is devoted to provide customers with LED application products. Synno has got through ISO9001 quality system certification of SGS of Switzerland, CE certification of European Union, GS certification, ROHS certification and relevant domestic LED lamps and lanterns certification.
outdoor led underground light, led inground buried light, recessrd underground light,underground buried light, underground step light
Jiangmen Synno Lighting Co., Ltd. , https://www.synnoled.com