Graphene has a unique nano-sheet structure and excellent electrical conductivity, mechanical properties and barrier properties. It is a research hotspot in the field of composite materials (coatings) in recent years. However, graphene is prone to agglomeration in a polymer resin matrix due to its high specific surface area and interlaminar force, and it is not possible to fully exert the excellent characteristics of graphene single layer or small layer, which limits its application in many fields.
The organic functional coating group directed by Wang Liping and Zhao Haichao, researcher of marine functional materials team of Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, is dedicated to the chemical and physical modification of graphene and the preparation and research of graphene multifunctional composite coating. The team based on the π-π interaction between graphene and conductive polymer, prepared a soluble conductive polymer by controlled polymerization, combined with ultrasonic dispersion to achieve liquid phase stripping of graphene, its dispersion concentration in organic solvents for conventional coatings. Up to 5 mg/mL, the average thickness of the graphene sheets after peeling was 2-3 nm (Fig. 1). Corrosion resistance and lubrication of a small amount of exfoliated graphene (0.5%) epoxy composite coating by passivation of the conductive polymer to the coating substrate and shielding and self-lubricating effect of the two-dimensional nanosheet structure of graphene Both sex and wear resistance have been greatly improved. Related work was published on Carbon and applied for national invention patents.
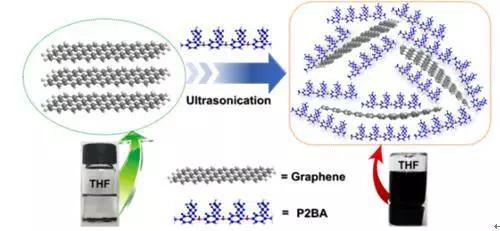
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of preparation of graphene dispersion
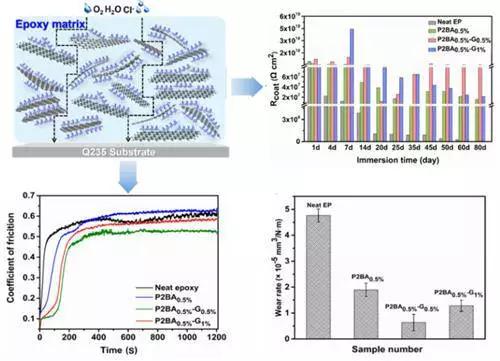
Figure II. Corrosion resistance and wear resistance of graphene modified composite coating
The hydrophobicity of graphene makes it difficult to achieve dispersion in water and aqueous resins. The team prepared water-soluble conductive polymer latex nanoparticles as intercalation agents for graphene by microemulsion polymerization (Fig. 3), which achieved stable dispersion of graphene two-dimensional nanosheets in aqueous resin. The layer, because the graphene forms a physical barrier layer in the matrix to prolong the diffusion path of the corrosive medium, and slows down the corrosion; the conductive polymer can form a dense passivation film on the metal surface, inhibit corrosion, and synergistically improve the corrosion resistance of the composite coating, and Studies by scanning vibrating electrode technology (SVET) have shown that the coating has self-healing properties (Figure 4). Related work is published on ACS Applied Material & Interfaces.
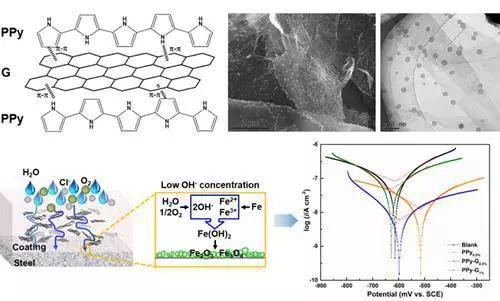
Figure 3. Structure and electron micrograph of graphene hybrids; Corrosion protection mechanism and corrosion resistance of hybrid composite coatings
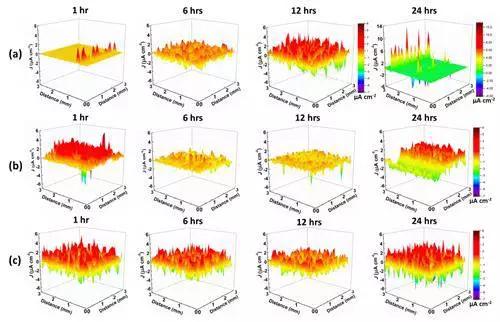
Figure 4. (a) Blank aqueous coating (b) Conductive polymer composite coating (c) Local current density distribution at the defect of graphene hybrid composite coating
The research work was supported by the “Hundred Talents Program†of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Frontier Scientific Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Major Technology Project of Graphene in Zhejiang Province, and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province.
Steel Cross,Stainless Steel Cross,Corbon Steel Cross,Pipe Fitting Cross
Cangzhou Youlong Pipe Fitting Manufacturing Co., LTD , https://www.ypco88.com