Lithium-ion batteries have become the first choice for energy storage in various industries, from mobile phones to cars, almost everything. However, its electrode material (Lithium/Li) is relatively rare, so mining and refining occupy the bulk of the cost. Over the years, we have been looking for more affordable alternatives. Researchers at Stanford University have turned their sights to ancient materials (salt/NaCl), whose newly developed sodium-ion batteries can store energy equivalent to lithium-ion batteries at less than 80% cost. !
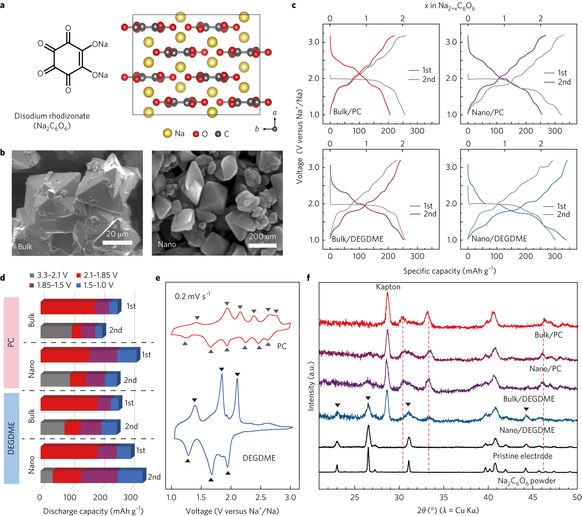
Figure 1: Na2C6O6 molecular structure and its electrochemical properties (inconsistent phase transitions) under different conditions in a nanocell.
Stanford University's newly developed sodium-ion battery has put lithium-ion batteries far behind in the cost of energy storage. The Earth has vast sources of sodium, such as the oceans and salt lakes, and sodium ions have undoubtedly become a perfect candidate for low-cost energy storage.
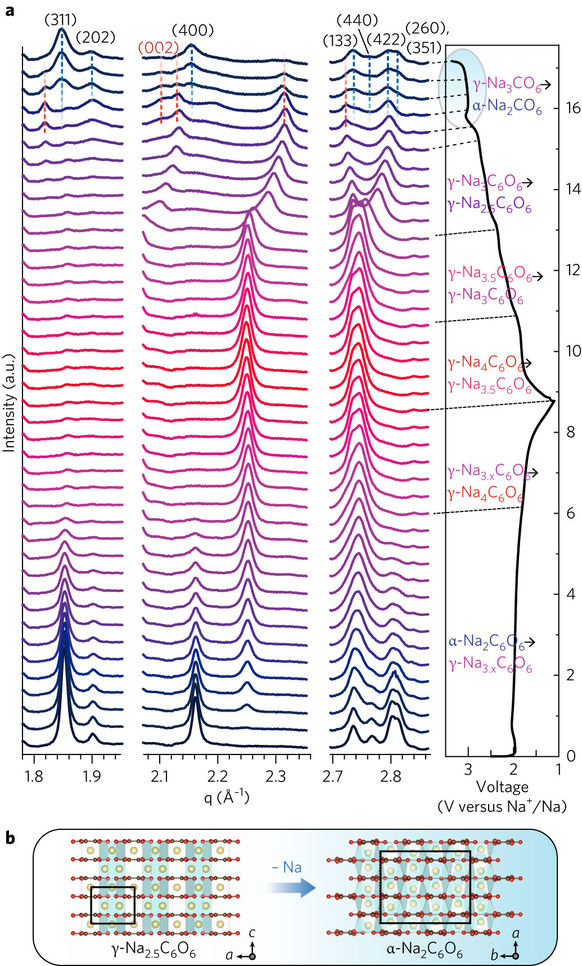
Figure 2: Phase shift of the Na2C6O6 sodium-de-sodium (inner-deserting) process.
In addition, sodium batteries can come in many forms, such as the 18650 batteries commonly found on notebook computers. Chief researcher Zhenan Bao said: "Performance, lithium is temporarily not yet able to find the opponent. But it is too expensive and too rare, so we need to develop a more abundant, more cost-effective sodium-based batteries."
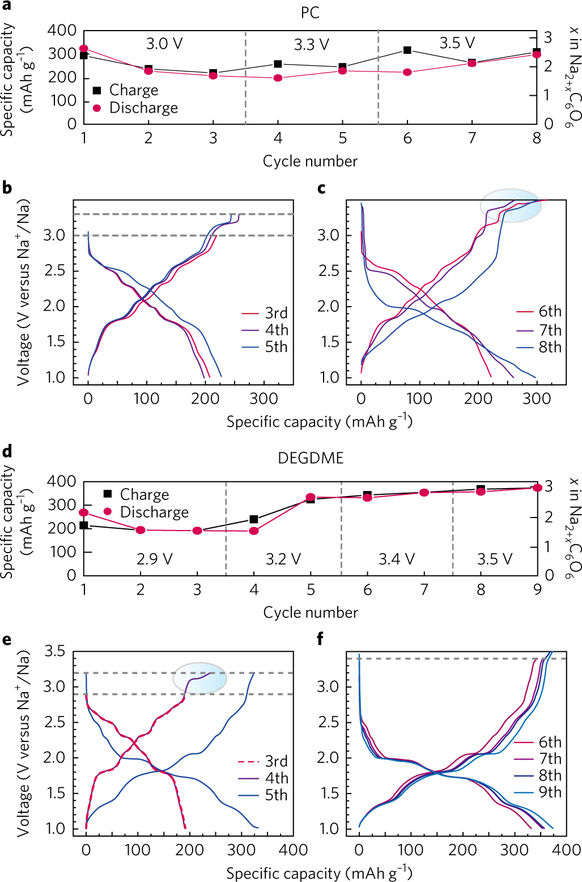
Figure 3: Change in voltage of Na2C6O6 during sodium-de-sodium removal (inner-desorption).
The Stanford team used a sodium salt electrode design to charge positively charged sodium ions toward negatively charged phosphorus anodes - both of which are abundant in nature. The researchers also stated that in order to improve the charge-discharge cycle, they analyzed the atomic force levels of sodium ions attached to and removed from the cathode during battery operation.
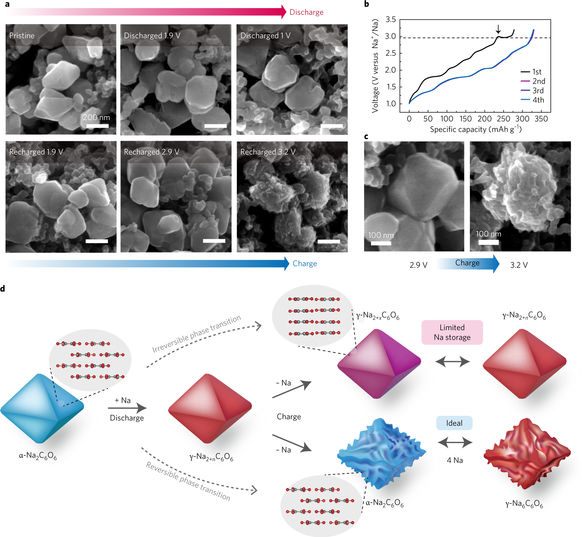
Figure 4: Morphological changes during reversible phase transition and the oxidation-reduction mechanism of Na2C6O6 sodium storage.
In the end, their sodium-ion batteries achieved a reversible capacity of up to 484 mAh/g and an energy density of 726 Wh/kg. The new battery's energy efficiency is said to exceed 87%. As for the most important cost aspect, the researchers claim that less than 80% of the investment can achieve the same storage capacity as lithium-ion batteries.
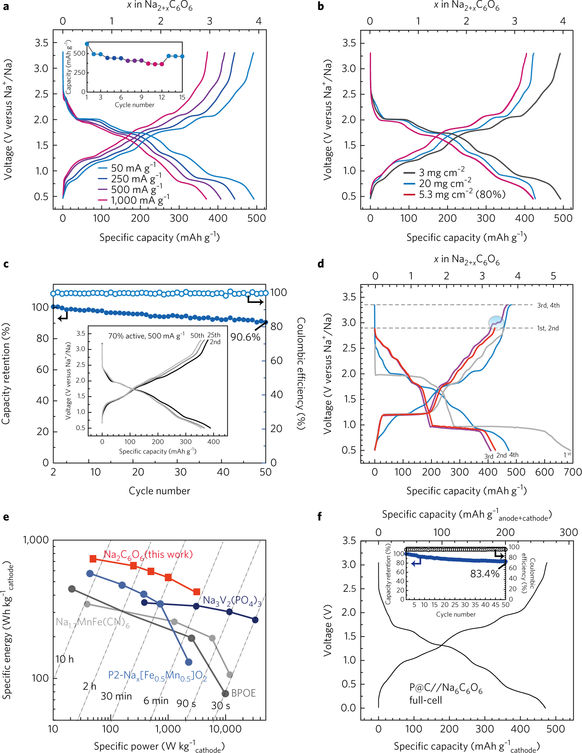
Figure 5: Electrochemical four-storage performance of Na2C6O6 electrode in half-cell and full-cell.
In the next step, the team will put more effort on the phosphor anode to squeeze out more performance of the sodium ion battery. Compared with lithium ions, the team also hopes to further increase the volumetric energy density of sodium-ion batteries. Details of this study have been published in the recently published journal Nature Energy.
Length 1.5M Soldering Wick,Soldering Remover Wire,Copper Desoldering Braid,Desoldering Braid Wire
NINGBO XIHAN TIN SOLDER CO.,LTD. , https://www.soldertop.com