The process of immersing steel parts in a solution containing manganese, iron, zinc, phosphoric acid, phosphate, and other chemicals to form a layer of poorly water-soluble phosphate conversion film on the surface of the metal is called phosphating. The phosphating process involves both chemical and electrochemical reactions.
Phosphating film layer has strong bonding with matrix, good adsorption, lubricity, corrosion resistance and electrical insulation. It is widely used in chemical production, automobile manufacturing, shipbuilding, machinery manufacturing, weapons, aerospace, aviation industry. Corrosion protection, lacquer bottom layer, lubrication, friction reduction, electrical insulation, etc.
The phosphating film is used as a corrosion protection film for steel. The earliest and reliable record is the patent obtained by Charles Ross in the United Kingdom in 1869 (B.P. No. 3119). Since then, the phosphating process has been applied to industrial production. In the long years of the past century, phosphating technology has accumulated rich experience and many major discoveries. During the First World War, the development center of phosphating technology was transferred from the United Kingdom to the United States. In 1909, the United States T. W. Coslet dissolved zinc, zinc oxide or zinc phosphate in phosphoric acid to make the first zinc-based phosphating solution. This research has greatly promoted the development of the phosphating process and broadened the development prospects of the phosphating process. The phosphating solution developed by Parker has overcome many shortcomings and shortened the phosphating time to less than 1 h. In 1929, Bonderizing reduced the phosphating time to 10 minutes. In 1934, the phosphating treatment technology was revolutionized in the industry, using a method of spraying phosphating solution onto a workpiece. After the end of the Second World War, phosphating technology rarely made breakthroughs, but only steadily developed and improved. During this period, important improvements in phosphating treatment technologies were: low-temperature phosphating, various methods for controlling the weight of phosphating membranes, and high-speed phosphating of continuous steel strips. At present, the research direction in the field of phosphating technology mainly focuses on improving quality, reducing environmental pollution and saving energy.
The appearance of the phosphating film exhibits a color such as light gray, dark gray, gray black or rainbow depending on the composition of the film layer. Phosphating membranes have various forms such as acicular orthorhombic crystals, cylindrical crystals, tetracentric crystals or mixed crystals, and amorphous crystals.The formation mechanism of the phosphating film is different from that of the phosphating system and the phosphating reaction mechanism of different substrates. Although researchers have done a lot of exploration in this area, they have not been fully clarified so far. Some researchers have used a chemical reaction equation to simply describe the phosphating film formation mechanism:
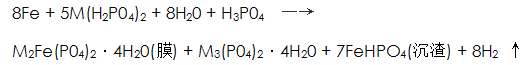
In the equation, M is Mn, Zn, Fe, or the like.
The steel is immersed in a high temperature solution containing phosphoric acid and dihydrogen phosphate to form a grained phosphate film composed of a phosphate precipitate, and produces iron hydrogen phosphate sediment and hydrogen. This mechanism is relatively crude and cannot completely resolve the film formation process.
Others believe that phosphating is carried out in a solution consisting of dihydrogen phosphate and phosphoric acid containing manganese, iron and zinc. Metal dihydrogen phosphate available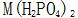 Said. During the phosphating process, the following chemical reactions occur:
Said. During the phosphating process, the following chemical reactions occur: 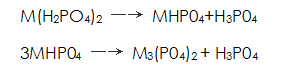
The above process can be expressed as an ion equation:
When the metal is in contact with the solution, near the interface where the metal surface is in contact with the solution,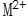 Increase in ion concentration or
Increase in ion concentration or 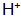 A decrease in concentration will cause the above reaction to move toward the formation of insoluble phosphate at a certain temperature.
A decrease in concentration will cause the above reaction to move toward the formation of insoluble phosphate at a certain temperature.
Since the metal dissolves in the phosphoric acid, the hydrogen ions are neutralized while releasing hydrogen, and a reaction occurs: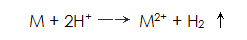
The water-insoluble phosphate formed by the reaction is deposited on the surface of the metal to form a phosphate protective film firmly bonded to the surface of the substrate.
From the electrochemical point of view, the formation of the phosphate film can be considered as a result of the action of the primary battery. On the cathode of the galvanic cell, a hydrogen ion reduction reaction occurs, and hydrogen gas is precipitated: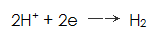
On the anode of the galvanic cell, iron is oxidized into ions into the solution and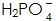 react.
react.
As the iron atoms continuously enter the solution to become ions, the pH gradually rises and the reaction proceeds to the right, eventually producing water-insoluble orthophosphate.
The above reaction can be expressed by the following program: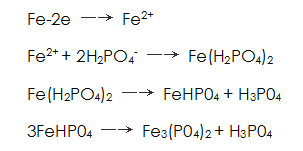
At the same time, in the solution near the anode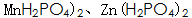 react:
react: 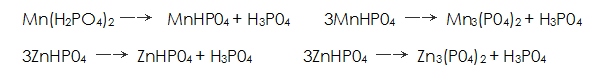
In this way, generated near the anode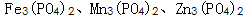 Together, the crystal adheres to the surface of the steel to form a phosphate film.
Together, the crystal adheres to the surface of the steel to form a phosphate film.
With the gradual deepening of phosphating research, scholars agree that the phosphating film formation process mainly consists of the following four steps:
(1) Acid corrosion causes the base metal surface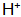 The concentration is lowered.
The concentration is lowered. 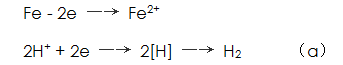
(2) Accelerator (oxidant) accelerates the interface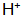 The concentration is further reduced rapidly.
The concentration is further reduced rapidly. 
Since the promoter oxidizes the hydrogen atoms generated by the first step reaction, the speed of the reaction (a) is accelerated, further leading to the metal surface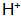 The concentration drops sharply. Also in the solution
The concentration drops sharply. Also in the solution 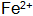 Oxidation
Oxidation 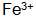 .
.
(3) Multistage dissociation of phosphate.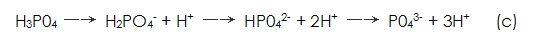
Due to the surface of the metal The concentration drops sharply, causing the equilibrium of the phosphates to shift to the right and eventually dissociate.
The concentration drops sharply, causing the equilibrium of the phosphates to shift to the right and eventually dissociate. 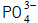 .
.
(4) Phosphate precipitates and crystallizes into a phosphate film.
When the metal surface is dissociated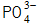 Metal ions near the interface with the metal in the solution, such as
Metal ions near the interface with the metal in the solution, such as 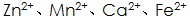 When the solubility product constant K sp is reached, a phosphate precipitate is formed, and the phosphate precipitates and crystallizes into a phosphate film.
When the solubility product constant K sp is reached, a phosphate precipitate is formed, and the phosphate precipitates and crystallizes into a phosphate film. 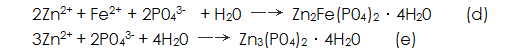
The phosphate precipitate forms a phosphating crystal nucleus together with water molecules, and the crystal nucleus gradually grows into a phosphating crystal grain, and numerous crystal grains are closely arranged to form a phosphate film. Different phosphating systems have different film forming mechanisms and will not be described in detail here.
Filter Series,Y Type Disc Filter,Y Type Water Filter,New Type Filter
Wenzhou KAIZHENG Valve Technology Co.,LTD. , https://www.kazevvalve.com