When cutting CCr12. Take V=76.4m/min, ap=1mm, f=0.2mm/r, and get Figure 5.
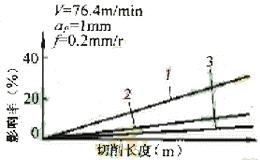
1. Natural cooling 2. Air cooling (-18 ° C) 3. Asian dry
Figure 5 Effect of non-cooling method on tool wear and dimensional accuracy when cutting GC12
When cutting with CCr12. Take V=52m/min, ap=1mm, f=0.2mm/r, and get Figure 6.
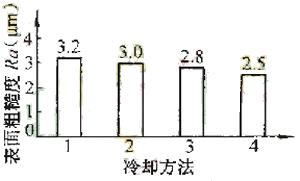
1. Natural cooling 2.-14 ° C cold air jet cooling 3. Sub-dry mode I (from the front knife jet) 4. Sub-dry mode II (simultaneous jet from the front and back flank)
Fig. 6 Relationship between surface roughness Ra and cooling method when cutting Cr12
When cutting 45 steel. Take V=70.4m/min, ap=1mm, f=0.2mm/r, and get Figure 7.
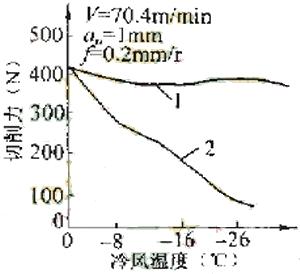
1. air-cooled 2. sub-dry
Fig. 7 Comparison of cutting force of cold air cooling when cutting 45 steel
Third, experimental analysis and theoretical discussion
1. Cutting force and cutting heat
It can be seen from Fig. 2 that in the low temperature region, the effect of casting cooling is better than that of air cooling; in the high temperature region, the effect of the air cooling is better than that of the casting cooling. It can be seen from Fig. 3 that in the natural cooling, air cooling (-15 ° C) and conventional cooling cutting, the natural cooling cutting force is the largest and the sub-dry cutting force is the smallest under the same process parameters. As can be seen from Fig. 4, in natural cooling, casting cooling, air cooling (-23 ° C) and sub-dry cutting, the cutting heat is sequentially reduced. This can be analyzed as follows:
Previous Next
Furniture Brackets and Connectors
Furniture Buckles,Drawer Knobs,Kitchen Cupboard Pulls Handles,Furniture Decorative Edge Handle
ChongQing Troya Hardware Manufacture Co., Ltd , https://www.troyahardware.com