In recent years, the development and industrialization of ABS/PC alloys have attracted the attention of the industry. The bulk ABS has low gel content, high compatibility and low impurity, and is suitable for the production of ABS/PC alloy, thereby broadening its application in the fields of home appliances, electronics and automobiles. In line with this opportunity, this paper discusses the current status of the bulk ABS resin industry, including the continuous bulk polymerization process and a number of new technologies available in the field.
Continuous bulk polymerization process has become one of the two mainstream production processes of ABS
Continuous bulk polymerization (referred to as B process) is a fast-growing ABS resin production process in recent years. Its production capacity is second only to emulsion graft-bulk SAN blending process (referred to as G process), and about 15%-20% of ABS products are produced. . The B process includes rubber variety selection, dissolution and filtration, prepolymerization, polymerization, devolatilization and granulation. The polybutadiene rubber is dissolved in a mixed monomer of styrene and acrylonitrile, and the rubber solution is continuously added to a plurality of series mixed full-flow or flat-push flow reactors in the presence of a small amount of solvent, and is continuously continuous after reaching a predetermined conversion rate. It is sent to the devolatilizer, and the unreacted monomer and solvent are flashed, cooled and recycled for recycling, and the molten material is further granulated into a finished product of ABS resin. Figure 1 is a block diagram of the B process flow.
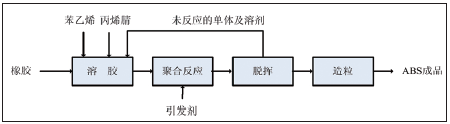
Figure 1 Process diagram of the production process of ABS resin B
The structure of the bulk ABS is basically the same as that of the GPPS, HIPS, and SAN polymerization reactors, and the post-processing facilities are similar. Therefore, the bulk ABS production device can also be used for the production of GPPS, HIPS, and SAN, making it a multi-functional production line with high cost performance.
The key technologies of the B process are three: the grafting of the monomer on the rubber before the phase transition occurs, the formation of the rubber particles during the phase transition, and the crosslinking of the rubber molecules during the post-treatment. 2 In the design of the polymerization reactor, the heat transfer, mass transfer and process control of high viscosity fluids should be solved. 3 In the performance of the resin, efforts were made to solve the problem of low rubber content and low gloss in the continuous bulk ABS.
From the perspective of reducing investment and operating costs, the B process has advantages. The technical and economic comparison between G and B processes is shown in Table 1.
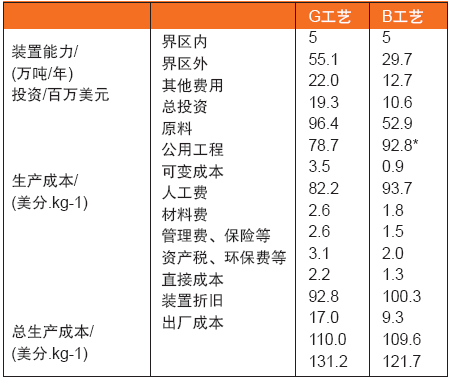
Table 1 Technical comparison of G process and B process technology (2012 level)
It can be seen from Table 1 that the use of imported rubber in the B process results in a slightly higher raw material cost, and the rest of the costs are lower than the G process, especially the project investment is about 45% lower, and the total production cost is also about 8% lower than the latter. When the scale of production is further expanded, the advantages of B process in project investment and production cost will be more obvious.
The raw material consumption and energy consumption of the B process and the G process are compared below, and the former is also low, as shown in Table 2.
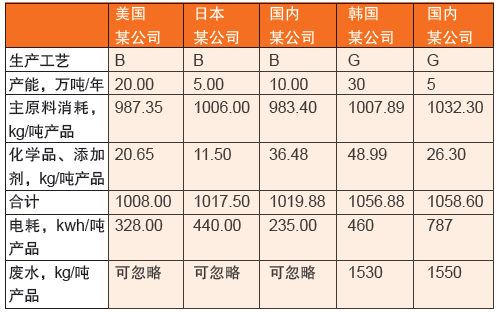
Table 2 Comparison of raw material consumption and energy consumption between B and G processes
However, the B process also has limitations, such as the rubber content of the product is generally less than 20% and the impact strength is low; the rubber particle size is large, and there is no high gloss and lively appearance of the G process product. Therefore, the application range of the B process product is relatively narrow. The research and development direction of the B process should be to increase the amount of rubber, control its particle size and its distribution to obtain higher impact resistance and gloss.
In order to better understand the structure and other characteristics of the B process product, further compare the two processes, see Table 3.
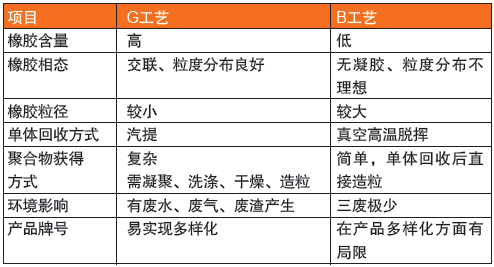
Table 3 G process and B process ABS product structure and other characteristics
In short, the B process has low investment, low operating cost, low energy consumption, and low emissions of three wastes. However, product performance is limited, you need to choose the right application, and ABS / PC alloy is a good choice.
B process research work is active, there are a number of new technologies available
In recent years, PetroChina Lanzhou Chemical Research Center, Dalian University of Technology, and Changchun University of Technology have also done a lot of experimental work on ontology ABS development. Kumho Rili, Blonde Technology and other successful applications of the body ABS in the automotive, electronic appliances and other fields. Yanshan Petrochemical Company, Dushanzi Petrochemical Company, Gaoqiao Petrochemical Company and other lithium rubber production plants carried out experimental research, and strived to provide qualified rubber raw materials for the bulk ABS production plant and achieved certain results, to name a few.
â—†Process innovation
基础Based on the traditional continuous bulk multi-tank polymerization process, after the first kettle, a strong stirring system is added to achieve the phase transformation of the material and control the rubber particle size within a suitable range, and then the material is sent to the subsequent polymerization kettle. The polymerization reaction is continued and devolatilization is carried out to produce an ABS resin product. The products produced by the method and the device have the advantages that the rubber particles are reduced, the distribution is significantly improved, the impact strength, the tensile strength and the gloss are improved, and the application range of the product can be broadened.
The styrene and acrylonitrile polybutadiene rubber solution is added to the first continuous stirred tank reactor in the presence of an organic peroxide, and the rubber grafting reaction is carried out at a predetermined temperature. The second continuous stirred tank reactor receives the reaction mixture from the first reactor for phase transformation and controls the particle size of the rubber particles. The third and fourth reactors convert more monomer and adjust the molecular weight of the product. The reacted polymer solution is delaminated by a multistage, multi-functional devolatilizer and the rubber is crosslinked to produce an ABS product having low volatility and rubber cross-linking. The bulk ABS resin produced by this process has excellent impact resistance.
In the presence of organic peroxide, the styrene and acrylonitrile rubber solution reacted at 90-170 ° C for 8-12 hours, and the material undergoes rubber grafting, graft rubber phase transformation, and the monomer conversion rate reaches 65%. -85%, the unreacted monomer and solvent in the polymer melt are removed to obtain an ABS product having a rubber content of 12% to 18%. The method can prepare high gloss, heat resistant series, high strength and easy processing products, and is suitable for making pipes, plates and the like, and is particularly suitable for manufacturing refrigerator linings.
â—†Making composite materials
◇ Made of PC, bulk ABS and polycarbonate-polysiloxane copolymer composite alloy, measured by ISO 180/1A at -40 ° C, with 36kJ / m 2 Izod impact strength, can be prepared by molding various impact resistance Products.
â—‡ Extinction grade ABS preparation. The styrene and acrylonitrile rubber solution are used as the main feed, and the remaining rubber solution is used as the auxiliary feed to carry out the polymerization reaction. By controlling the particle size and distribution of the rubber particles, the rubber type, the rubber content and the feed ratio, the extinction level is obtained. ABS resin, and the product has high impact strength and good processing performance, suitable for making injection molded parts such as electronics, toys and home appliances.
â—‡ABS/PBT compound. It consists of the following raw materials: bulk ABS 30%-70% (mass, the same below), PBT 5%-30%, compatibilizer 2%-8%, heat-resistant modifier 0.5%-5%, glass fiber 10 %-35%. The material is fully melted and compounded under high-speed shearing, mixing and conveying of the screw, and the product is obtained by melt extrusion, cooling, dicing, and drying. The process can impart high strength, fatigue resistance and impact resistance to the bulk ABS, and expand the application range thereof.
◇ Automotive body ABS modified material and its preparation method. The components (weight percentage) of the modified material: ABS 64.0% - 88.7%, heat-resistant modifier 10% - 30%, light stabilizer 0.3% - 1.0%, heat stabilizer 0.3% - 1.0%, silicone Masterbatch 0.5%-3%, processing aid 0.2%-1%. The surface gloss of the product is 20%, the odor level is 2-3 grades of Volkswagen, the Vicat softening temperature is 118 °C, the low organic volatiles, scratch resistance, can fully meet the interior material requirements of the automobile OEM.
Low odor, flame retardant bulk ABS composite. Composition (weight percentage) of the following materials: bulk ABS 58.0%-86.5%, heat-resistant modifier 10%-24%, UV absorber 0.3%-1.0%, silicone masterbatch 0.5%-3%, odor suppression The agent is 0.5%-5%, the flame retardant is 2%-8%, the lubricant is 0.1%-1%, and the coupling agent is 0.1%-1%. The material was dry mixed in a high speed mixer for 3-5 minutes, placed in a twin screw extruder, melt extruded, and pelletized. During the extrusion process, the heat-resistant modifier is metered uniformly through the side-by-side precise feeding system of the extruder, and the product is obtained by extrusion, cooling, pelletizing, and drying. This product has low odor and superior flame retardant properties, making it suitable for automotive interior parts, refrigerators and electronic and electrical components.
Domestic on-body ABS has a certain scale, but the installation rate is not high.
The continuous body process belongs to the clean production process and conforms to the sustainable development strategy. It is the ABS production process encouraged by the state. Many manufacturers and institutes at home and abroad have attached great importance to the research and development of continuous bulk polymerization technology, and have emerged from Dow Chemical, Japan Mitsui Chemicals (formerly Japan MTC), German Lanxess (taken over US Monsanto technology), Sinochem International, etc. Manufacturers with mature technology, the main companies in the world producing continuous ontology ABS in 2011 are shown in Table 4.
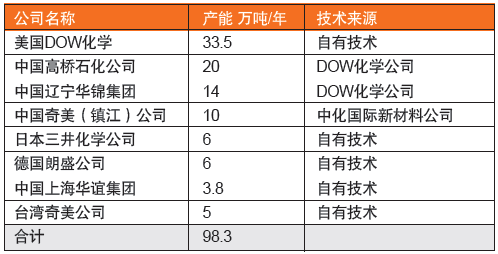
Table 4 List of major companies in the world of continuous production ABS (2011)
In 2006, Gaoqiao Petrochemical Company introduced DOW chemical technology to build a 200,000 tons/year bulk ABS unit, which was put into operation in 2007. China Ordnance Industry Group Liaoning Huajin Chemical (Group) Co., Ltd. introduced DOW chemical ontology ABS technology in 2008 and built a 140,000 tons/year plant, which was put into operation in November 2010. In 2007, Chi Mei (Zhenjiang) purchased the technology of Sinochem International New Materials Co., Ltd. to build an annual output of 100,000 tons of equipment and put it into production in November 2009. Shanghai Huayi Polymer Co., Ltd. uses its own series of fully mixed polymerization reactors (CSTR) technology. In 2011, it built a 38,000 tons/year plant.
Although the bulk ABS product grade is not as much as the emulsion grafting-bulk SAN blending method, it has also formed its own product series by adjusting the formulation and process. The product grades of the main producers of the main body ABS in 2011 are shown in Table 5.
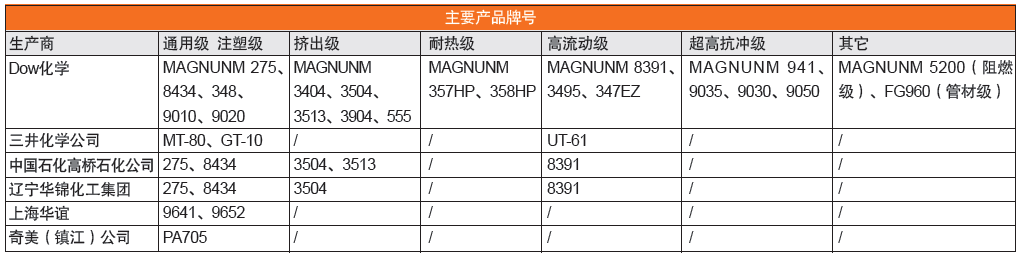
Table 5 Main ABS main product grades
DOW chemical products are the most complete, both general-purpose products, heat-resistant grades, ultra-high impact grades and other special grades, but they generally only transfer general-purpose production technology when transferring technology. The bulk ABS resin produced by domestic enterprises is mostly general-purpose products, lacking high-performance special material grades.
After many years of hard work, Gaoqiao Petrochemical Company has made great contributions to the promotion and application of ontology ABS products and the development of the Chinese market. The operating rate of its installations has increased year by year. However, the operation rate of other similar devices in China is low and the situation is rampant.
Magnesium Fluoride (MgF2) Windows offer excellent broadband transmission from the deep-UV to the mid-infrared.
MgF2 is a rugged material resistant to chemical etching, laser damage, and mechanical and thermal shock.
MgF2 exhibits excellent broadband transmission from 120 nm to 8 μm , from the deep UV to the mid infrared. This makes them a good choice for UV radiation sources and receivers as well as for use at the Hydrogen Lyman-alpha line. They are often used as UV viewpoints, and are a good option for UV polarizers and excimer laser applications. It has a high transmittance between 120 nm and 8 µm, and between 0.4-5.0 µm transmits over 90%.
MgF2 has a melting point of 1255 degrees Celsius. It has a density of 3.177 g/cm3, and a tetragonal crystal type. Our optical windows are typically oriented with the round surfaces perpendicular to the c-axis of the MgF2 crystal to minimize birefringence. Custom random cut MgF2 windows can be manufactured on request.
MgF2 is the only optical material which combines a wide spectral transmission band with birefringence. This birefringence means that the refractive index depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. Because of birefringence, a MgF2 window can exhibit double refraction, so that a ray of light will be split by polarization into two rays with different paths.
- Excellent Transmission from 120nm to 7μm
- Rugged and Durable
- Resistant to Chemical Etching


Mgf2 Window, Crystal Mgf2 Lens,Mgf2 cylindrica lens
Changchun Ruiqi Optoelectronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.ruiqi-optics.com