1 Which metal can be welded by Ar+He mixed gas TIG welding?
The arc of Ar+He mixed gas has the synthetic performance of argon gas and helium gas, has the cooperation and purification effect of high stable arc and high heat power, and is beneficial to reduce pores, has high arc temperature, and can obtain more workpieces. The heat, the penetration depth is large, and the welding speed is almost twice that of argon arc welding. Ar+He mixed gas TIG welding is suitable for welding aluminum and aluminum alloys, magnesium and magnesium alloys, copper and copper alloys, titanium and titanium alloys, and metal-based (usually aluminum, magnesium, titanium, etc.) composite materials.
What are the characteristics of 2 Ar+He mixed gas arc?
The argon density is larger than air, and the specific heat capacity and thermal conductivity are smaller than air. These characteristics make argon have good protection and arc stabilization. Compared with argon gas, the helium gas has high ionization potential and large thermal conductivity. Under the same welding current and arc length, the arc voltage of the xenon arc is higher than the argon arc (that is, the electric field strength of the arc is high), which makes the arc larger. The power of the helium gas is good, so that the arc energy density is large, the arc column is fine and concentrated, and the obtained weld has a large penetration rate.
What is the effect of the 3 Ar+He mixture ratio on the arc characteristics?
As the gas ratio changes, the shape of the arc changes. The effect of the volume fraction of helium on the shape of the arc is shown in Figure 1-6. When the photo is welded with magnesium alloy, the digital camera and the welding filter lens are used, and the distance between the camera lens and the arc is constant. It can be seen from Fig. 1-6 that as the proportion of helium in the mixed gas increases, the arc gradually shrinks, especially when it is pure helium, the arc shape is significantly changed compared with pure argon, and the arc shrinks seriously. The arc column is thin and concentrated. The color of the arc gradually changes from white to orange, which is mainly due to the fact that the spectrum of pure helium is in the orange wavelength range. As the proportion of helium increases, the number of ionization and recombination of helium in the arc increases gradually. The relative intensity also increases, and the color of the arc gradually changes from white to orange.

The stability of the arc decreases with the increase of the proportion of helium. When the integral number of helium gas exceeds 70%, the arc is difficult, the arc is unstable, and the protection effect is poor. When the gas integral number is 90%, the molten pool splashes seriously; When the gas number of the helium gas reaches 90% or more, the arc ignition is extremely difficult, and the arc during the welding process is extremely unstable.
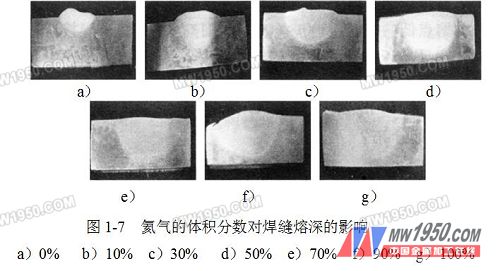
What is the effect of 4 Ar+He mixed gas ratio on weld penetration?
The effect of the volume fraction of helium on the weld penetration is shown in Figure 1-7. This figure is a photograph of the penetration of a magnesium alloy weld. It can be seen from Fig. 1-7 that as the proportion of helium in the mixed gas increases, the penetration depth gradually increases and the shape changes from mushroom to flat, but when the gas number of the helium gas exceeds 50%, the melting Deep changes are slower. This is because the power of the xenon arc is larger than that of the argon arc. As the helium gas increases, the arc energy density increases, the arc shrinks, and the penetration rate increases, resulting in a large penetration. However, due to the thickness of the workpiece and the constraints of the welding, the penetration depth does not change significantly after reaching a depth of about 6.5 mm.
What is the effect of the 5 Ar+He mixture ratio on the operability of the weld?
As the proportion of helium increases, the splash in the molten pool becomes more severe and the welding fumes increase. When the volume fraction of helium reaches 90%, the magnesium alloy evaporates severely, the welding fumes are large, the operator has dizziness, chest tightness, and nausea, and it is basically impossible to achieve normal welding. From the practicality, economy and environmental protection of welding, in the Ar+He mixed shielding gas, the welding of magnesium alloy can be carried out by using helium gas with a volume fraction of 30% to 50%.
What is the joint structure of 6 Ar+He mixed gas TIG welded magnesium alloy?
When the TIG welding of the magnesium alloy is carried out by using the Ar+He mixed gas with a volume ratio of 1:1, the arc is stable during the welding process, the cathode cleaning effect is obvious, the oxide film is easily broken, the molten pool is sufficiently stirred, and the protective atmosphere is good. Compared with the base metal, the grains in the heat-affected zone are coarser. The weld zone is organized into small equiaxed grains with obvious characteristics of rapid solidification structure, and the grain size is obviously smaller than that of the base material zone and the heat affected zone. This is mainly related to the thermal cycling process of TIG welding and the physical properties of magnesium alloys. During the welding process, the base material in the weld zone absorbs a large amount of heat and melts. Due to the large thermal conductivity of the magnesium alloy during solidification, the heat dissipation is fast, which promotes the rapid solidification and crystallization of the metal in the weld zone, resulting in the weld zone. Grain Refinement. In addition, the molten pool agitation also promotes the growth of equiaxed grains in the weld zone. The coarse grain in the heat-affected zone is due to the low melting point of the magnesium alloy (generally in the range of 500-600 ° C), fast heat conduction, wide heat-affected zone caused by welding and easy to overheat, and the absorbed heat causes the microstructure of the heat-affected zone to occur. The grain grows, resulting in coarse grain formation in the heat affected zone.
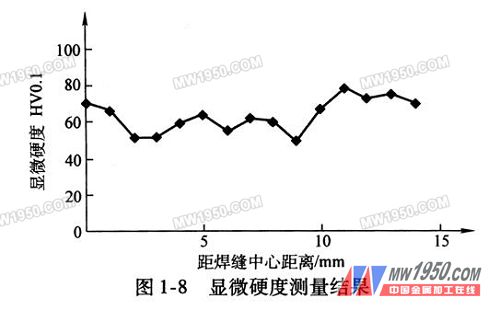
How is the microhardness of the joint of 7 Ar+He mixed gas TIG welded magnesium alloy distributed?
The microhardness measurement results of the weld, heat affected zone and base metal zone are shown in Figure 1-8. It can be seen from the figure that the hardness of the weld zone is slightly lower than that of the base metal, but the difference is not large. The hardness of the joint between the weld and the thermal shadow zone is obviously increased, and the hardness of the heat affected zone is obviously lower than that of the base metal. Since the grains in the heat-affected zone are coarser, according to the Hall-Petch formula, the microhardness of the heat-affected zone is low. In the weld zone, on the one hand, the remarkable refinement of the microstructure increases the microhardness; on the other hand, compared with the formed Mg17Al12, when the A1 element is mainly in the solid solution state, the microhardness is lowered. Under the combined effect of the two factors, the microhardness of the weld zone is close to the base metal zone.
What is the joint strength of 8 Ar+He mixed gas TIG welded magnesium alloy?
When TIG welding is carried out with a volume ratio of 1:1 Ar+He mixed gas for the protective atmosphere, the tensile strength of the weld is 184 MPa, and the tensile strength of the base material is 268 MPa, and the tensile strength of the weld reaches the base material. 68% of the joints have an elongation of 58% of the base metal, which is significantly lower than that of the base metal.
From the macroscopic section, the fracture of the tensile joint of the welded joint occurs in the heat-affected zone, the surface of the fracture is rough and the color is gray, but there is no obvious necking before the fracture; the fracture of the base metal occurs in the middle of the gauge length, and the fracture The base metal is at an angle of 45°.
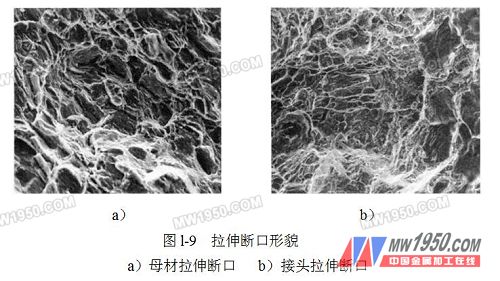
Figure 1-9a shows the scanned image of the tensile fracture of the base metal, and Figure 1-9b shows the scanned image of the tensile fracture of the joint. It is found from the figure that the base metal belongs to ductile fracture; the fracture is mainly composed of plastic pit, which is ductile fracture; and the joint fracture is a mixed fracture composed of cleavage and plastic pit, which is a tough-brittle mixed fracture.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of 9 Ar+He mixed gas TIG welding magnesium and aluminum alloy?
1) Make full use of AC argon arc welding equipment to expand its range of use.
2) The operation is simple, the weld bead is beautifully formed, the quality is excellent, and the mechanical properties meet the requirements for use.
3) The welding heat input is small, and the weld and heat affected zone are fine and uniform.
4) It is more suitable for repairing thick aluminum alloy parts with higher requirements, and can reduce the pores.
5) The cost is higher.
Is 10 Ar+He mixed gas TIG welding harmful to humans?
Both Ar and He are inert gases, which are non-toxic and do not react after mixing. Therefore, TIG welding with Ar+He mixed gas does not cause harm to the human body. However, when the magnesium alloy is welded with the Ar+He mixed gas TIG, the operator may feel uncomfortable at the beginning, especially in the stomach. This is not the reason for the Ar+He mixed gas, which is caused by the stimulation of the human body by the magnesium vapor. There will be a significant improvement after 1 week of normal operation, but measures such as wearing a mask are required.
How to determine the welding parameters of 11 Ar+He mixed gas TIG welding magnesium alloy sheet?
Since the magnesium alloy has the characteristics of low melting point, high thermal conductivity, high coefficient of linear expansion, and small surface tension, the welding method is strict. TIG welding of tungsten-mixed gases enables high-quality welding to produce beautiful, smooth, high-quality welds.
1) TIG welding was performed under a protective atmosphere in which Ar and He were at a volume ratio of 1:1.
2) Welding current. Under the condition that other welding parameters are constant, a welding current of 40 to 100 A is selected for the magnesium alloy sheet having a thickness of 3 mm. When the current is small (≤50A), unfused and incomplete penetration, partial collapse and protrusion of the weld surface are prone to occur. When the current is too large (≥60A), the base metal is deformed greatly, and burnt through is easy. The weld has defects such as over-burning, pores, cracks, etc. The wire is melted before the weld, and the droplet solidifies at the end of the wire. , hindering further filling. When the current is appropriate (50~60A), the formed weld surface is smooth, no pile height, beautiful appearance and good quality.
3) Welding speed. When the welding speed is less than 10cm/min, the line energy input to the base metal is more. At the same time, due to the high vapor pressure of the magnesium alloy, the surface tension is small, and defects such as welding leakage, undercut and deformation are easily caused during welding, and the weld seam and The grains near the weld zone are significantly grown.
When welding is carried out with a large welding speed (14 cm/min), the stability of the arc can be improved, and a good weld appearance can be obtained.
4) Arc height. When welding, the arc height should be kept as low as possible, the arc cathode crushing effect should be fully exerted, and the molten pool should be fully stirred to promote the escape of oxides and hydrogen. Under normal circumstances, when the arc height is 4mm, the ideal welding effect can be achieved, and the wire filling is convenient.
What are the characteristics of 12 Ar+He mixed gas welded aluminum alloy?
1) When welding thick aluminum alloy material, the He+Ar mixed gas as the shielding gas can significantly increase the heat input to the weld, increase the effective penetration of the weld, and improve the metal deposition efficiency. As the proportion of He increases, the penetration depth of the weld can be significantly improved. When the thickness of the plate is increased, the amount of He added should also be increased accordingly.
2) When high-current MIG welding thick plate aluminum alloy material, with the increase of welding current, the inert gas protection fails and the outside air enters the welding area (welding arc and welding pool), which affects the welding arc and makes the arc impossible. Stable combustion; on the other hand, oxygen and nitrogen in the air enter the weld pool and chemically react with the molten aluminum. In addition, a large amount of heat causes the weld pool to be in a state of severe overheating, and the effect of the arc force eventually causes the weld to wrinkle. Compared with pure Ar as the shielding gas, the He+Ar mixed gas can significantly increase the critical current value of the wrinkles in the weld and reduce the tendency of wrinkles in the welding process.
The above content is excerpted from the "Special Welding Technology Q&A" published by Mechanical Industry Press.
Author: Liu Sheng new editor ISBN: 978-7-111-25878-0
Book price: 30.00 yuan (including postage)
Book content consultation telephone-88379405
Book purchase phone ~98-709 娄 teacher
Post office remittance:
Address: "Metal Processing" magazine, No. 22, Mianzhuang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, China Postcode: 100037
Call to 709
Fax Email:
Bank transfer:
Bank: Bank of China Industrial and Commercial Bank Million Village Branch Account Name: Machinery Industry Information Research Institute Contact: Yan Pingzheng Wang Lei (in the postscript column, must indicate the "metal processing" magazine book)
Fiberglass Measuring Tape,Fiberglass Tapes Measure,Fiberglass Tape Measure,Plastic Fiberglass Measuring Tape
Shangqiu Hengli Measuring Tools Co.,Ltd , https://www.jjmtools.com